COVID-19 Austere Pocket Guide
Joint Trauma System
Command & Force Protection Considerations
- Prevention of COVID-19 transmission to medical personnel is mission critical to preserve wartime, trauma care capability
- Closely manage & conserve equipment & supplies including oxygen, ventilators, sedation medications, & personal protective equipment.
- Expect reduction in supply lines with limited resupply or delivery.
- Expect delayed medical evacuation due to decreased transport availability, airspace restrictions, & reduced military asset access.
- Initially plan for 1- 3 critically ill COVID-19 patients at each austere location.
- Quarantine is a unit/command function, requiring medical support, that separates and restricts movement of those unknowingly exposed to a contagious disease without symptoms.
- Isolation is medical function, requiring command support, separating those with contagious disease symptoms from people who are not sick.
- Patient Under Investigation (PUI) require medical isolation due to signs/symptoms of COVID-19 & history of potential exposure.
- Communicate PUI’s to medical and operational leadership on identification & their potential close contacts.
- Communicate identified PUI’s and close contacts via 5Ws format to command surgeon (or designee), following unit notification & theater surveillance policies.
- Pre-designate primary COVID provider to perform all COVID-19 evaluations and coordinate procedures to limit medical personnel exposure, retaining combat casualty care effectiveness.
- Designation should balance provider skills and experience with potential impact on medical support for combat operations.
- Designated provider may not be the most experienced and should consult with team as needed for management, procedures, and nursing care.
- A pandemic may require establishment of medical rules of engagement that discourage initiation of CPR due to aerosolization and high risk of cross-contamination.Begin early evacuation coordination for high risk patients.
Triage & Hemorrhage Control
- Identify Persons Under Investigation: fever >38C/100.4F) & one of the following: cough, shortness of breath, respiratory accessory muscle use, loss of smell, history of exposure to wide-spread COVID-19 areas within 14 days of symptoms, or known exposure to known COVID-19 areas within 14 days of symptoms
- Recognize & consider early evacuation for those at risk of severe disease including mild COVID-19 symptoms, normal SpO2, but with shortness of breath; use of accessory muscles; age over 45 years; chronic disease (obesity, cardiovascular, & pulmonary)
- Primary medical mission remains damage control resuscitation and damage control surgery.
- Those severely ill may develop excessive blood clotting and be at increased risk for venous and arterial thrombosis
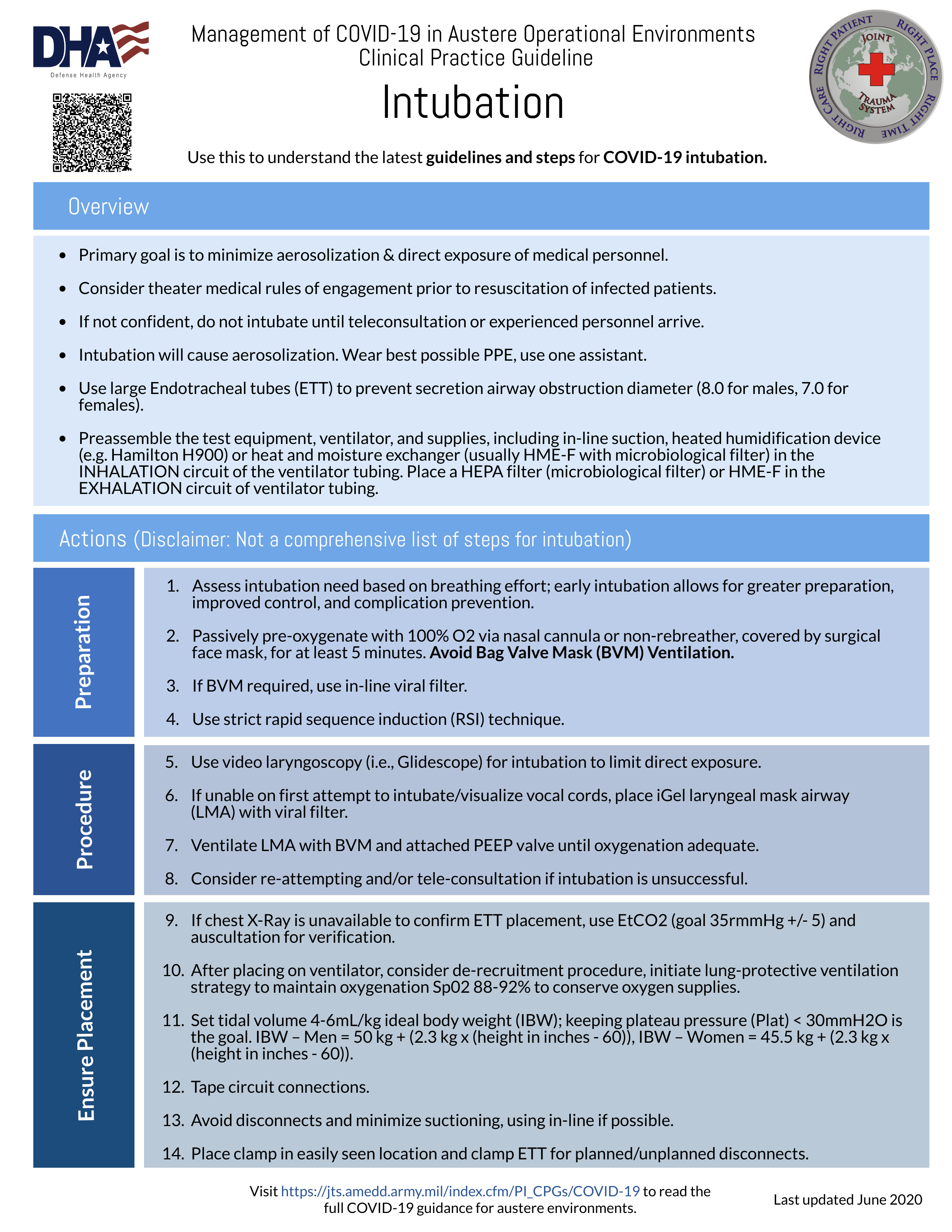
Airway Considerations & Management
- Do not intubate unless confident to perform procedure, consider use of teleconsultation or wait for personnel who can provide advanced airway management.
- Minimize aerosol & exposure of medical personnel to preserve deployed trauma care capacity.
- Always wear best available PPE for intubation and aerosolizing procedures, ensure hand hygiene.
- Assess intubation need based upon work of breathing. Early intubation may allow a controlled intubation, preventing complications.
- COVID19 patients usually present with intact airways and do not need cricothyroidotomy.
- Better to choose early intra-theater critical care facility transfer over early cricothyroidotomy.
- Cricothyroidotomy without ventilator use consumes scarce resources (manpower required to bag-ventilate the patient with PEEP, inefficient delivery of oxygen via bag-ventilation, & increases aerosolization risk.
- Limit intubation procedure to one additional PPE-protected assistant at least 2 meters away.
- Passively pre-oxygenate with 100% O2 for at least 5 minutes. Place surgical mask on the patient, on top of nasal cannula or NRB mask, if tolerated.
- Use strict RSI technique – do not use bag-valve-mask ventilation if possible. If using BVM, place viral filter in-line if available.
- Use video laryngoscopic-guided intubation (Glidescope) if available to minimize health care personnel exposure. If unable to intubate or obtain vocal cord visualization on first pass, consider the placement of an iGel LMA with viral filter.
- Ventilate with the BVM and PEEP valve until oxygenation is adequate. Then, consider re-attempting and/or teleconsultation.
- Check EtCO2 and auscultation to confirm placement since chest X-Ray may not be available to confirm tube placement.
- Place as largest endotracheal tube possible as secretions may be an issue.
- Use heated humidification device (e.g. Hamilton H900) or heat and moisture exchanger (usually HME-F with microbiological filter) via INHALATION circuit of the ventilator tubing if available.
- Use HEPA filter (microbiological filter) or HME-F via EXAHALTION circuit of ventilator tubing if available.
Ventilation Considerations & Management
- Position with head of bed elevated, self-proning of non-ventilated conscious patients may improve ventilation and secretion management. Awake self-proning with high flow nasal cannula or nonrebreather may delay/prevent intubation.
- Sp02 goal 92% if conservation needed for oxygen supplies. Use surgical face mask over prongs/nonrebreather if possible. However, prone positioning poorly tolerated, DO NOT force position.
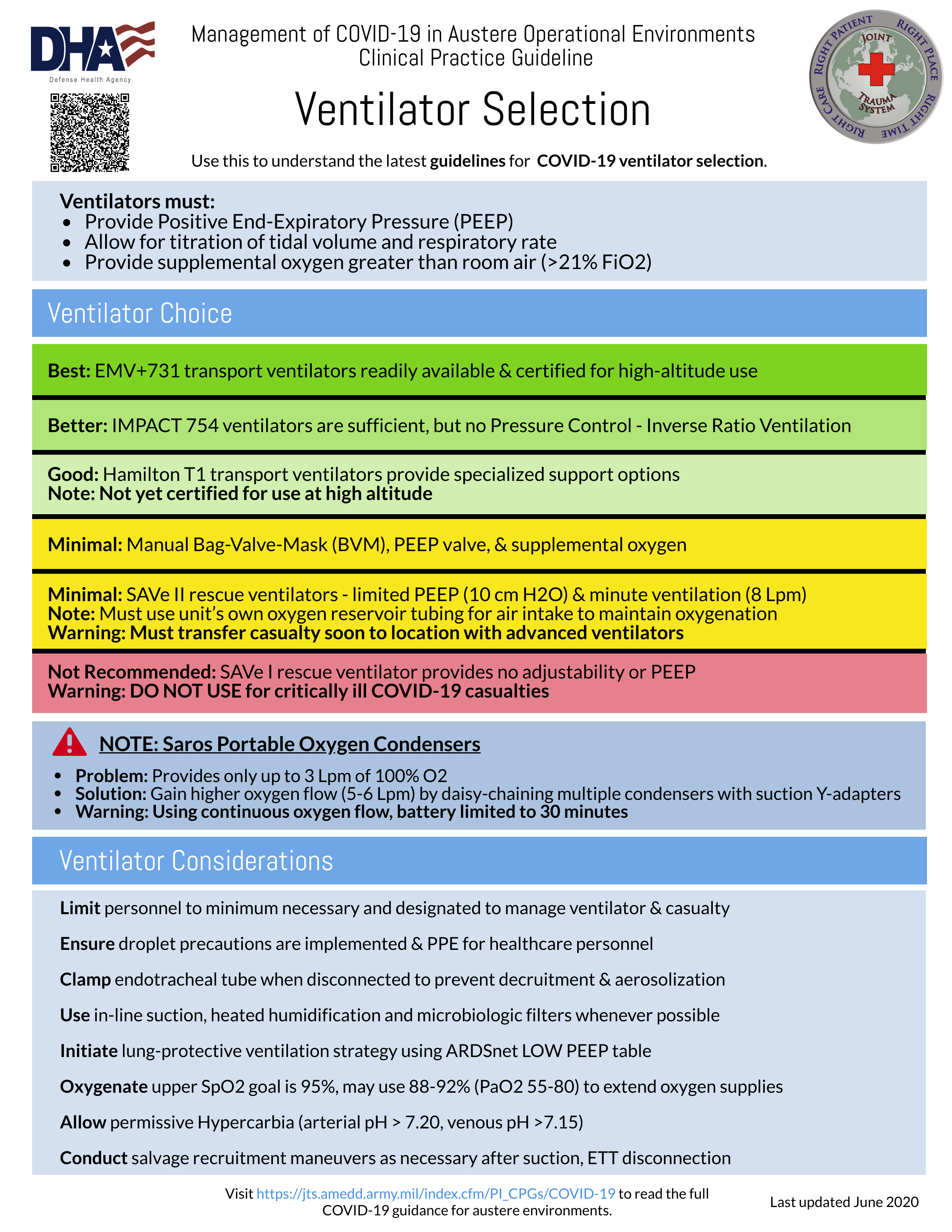
- Initiate lung-protective ventilation strategy for those requiring mechanical ventilation. Use the ARDSnet LOW PEEP table.
- Ventilate with tidal volume 4-6mL/kg ideal body weight (IBW) keeping plateau pressure (Plat) < 30mmH2O as goal
- Maintain OSpO2 88-92% or PaO2 55-80mmHg (Note: ARDSNet recommends SpO2 upper limit of 95%; targeting 92% is reasonable to extend oxygen supplies)
- Permissive hypercarbia (arterial pH > 7.20, venous pH >7.15)
- If ETT must be disconnected from the ventilator for ANY reason, clamp the ETT to prevent decruitment and minimize aerosolization of the virus.
- If in-line suction devices are not available, de-recruitment will likely occur with suctioning. Salvage recruitment maneuvers may be necessary.

- Change upper limit of Peak Inspiratory Pressure (PIP) alarm to 50cmH20;
- Decrease tidal volume as low as possible (50mL);
- Increase PEEP to 30-40cmH20;
- Hold for 40 seconds (if signs of hemodynamic instability develop, stop the recruitment maneuver, and resume prior settings);
- Increase PEEP to 2cmH20 ABOVE prior PEEP setting;
- Increase tidal volume back to prior setting;
- Return upper limit of PIP alarm to prior setting;
- Monitor hemodynamic instability or high PIP, indicates possible pneumothorax.
- Escalate PEEP to 14cmH20 as aggressively as possible as hemodynamics allow to optimize oxygenation, minimize FiO2 needs, and extend oxygen supply.
- Use the ARDSNet Protocol LOW PEEP table as a guide for further titration of PEEP.
- Be prepared to start vasopressors and extremely judicious use of IVF to support pre-load in the face of high PEEP (aka PEEP tamponade).
- Consider a combination of paralysis and prone positioning early to lengthen duration of available oxygen supply.
- Consider Inverse Ration Ventilation (IRV) once patient reaches PEEP 18cmH20 on the LOW PEEP table.
- EtCO2 goal is 35mmHg +/- 5. Obtain ABG if available (iStat), obtain baseline PCO2, correlate with EtCO2. Note: (EtCO2 of 40 may actually represent PCO2 of 60 with a 7.24 pH in pulmonary disease.)
- Manual breath button on the bottom left of EMV+731 & allows for manual measurement of plateau pressure (Pplat). The Pplat goal is less than 30cmH2O. In the absence of Pplat, a PIP target of less than 35cmH20 is desired.
- If Pplat is greater than 30cmH20, decrease set tidal volume by 1 mL/kg steps (generally about 50-80 mL). Titrate set respiratory rate (RR) up increments of 2 bpm to maintain pH and EtCO2 at goal. Avoid RR above 30 bpm given significant risk for breath stacking and auto PEEP.
- Consider serial blood gas evaluation via iStat (adjusting frequency to patient stability).
- Increased secretions & mucous plugging are extremely common causes for increased oxygen requirement, difficulty with ventilation, and respiratory failure.
- Secretions are heavier than usual. Use in-line suction (closed system), which minimizes aerosolization and de-recruitment, but not often available in austere settings.
- Use heated humidification to prevent drying out of secretions and promotes sputum clearance.
- Heated-humidification devices are equipment designed to be used along with ventilators (e.g. Hamilton H900).
- Heat-Moisture Exchangers (HME) are supplies that fit in-line with the ventilator tubing and trap heat and moisture within the circuit.
- Heat-Moisture Exchange Filters (HME-F) are supplies that fit in-line with the ventilator tubing and provide HME and microbiologic filtration.
- Pre-treat with albuterol and/or ipratropium for 10-15 minutes
- 20% N-acetylcystine (Mucomyst) as 1-2mL direct instillation into ETT every 6 hours as needed for secretion control
- 3% Saline (Hypertonic Saline) as 5mL direct instillation into the ETT every 12 hours as needed for secretion control
- Use bronchodialators with caution. Albuterol and ipratropium effectively dry up secretions but they may increase mucous plugging.
- Anti-Sialagogues not routinely recommended for COVID-19 patients.
There is no single strategy recommended for management of severe ARDS. Many interventions are due to resource constraints within austere environments. If unfamiliar with these techniques, obtain teleconsultation guidance.
- As more of the breath cycle will be spent in inspiration, ventilation may worsen with a transition to PC-IRV.
- EMV+731 with the most recent software package has the capability to do PC-IRV. While using AC-P mode, PC-IRV is achieved by increasing the I:E ratio above 1:2 (i.e. 1:1, 2:1, 3:1 and higher).
- PC-IRV cannot fully approximate Airway Pressure Release Ventilation (APRV), but is still the best available salvage mode using EMV+731.
- Once PEEP is maximized (or limited by peak inspiratory pressure) and oxygenation is still not yet at goal, increase the I:E ratio incrementally.
- Tidal volume goals remain the same as with conventional ventilation; adjust cycle time (60/RR) to optimize minute ventilation.
- As higher I:E ratios are non-physiologic, PC-IRV may require increased sedation for patient comfort and synchrony.
Resuscitation
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) in an austere environment is not an appropriate use of resources unless the etiology for the arrest is immediately apparent and/or rapidly reversible.
- Significant aerosol generation occurs during CPR of a COVID-19 patient. Anticipate providers involved will become infected with disease.
- If CPR is performed, the wear best available PPE before patient contact, surgical mask placed over patient’s airway until a definitive airway is secured, & the number of PPE protected personnel involved should be minimized to 1 or 2.
- Coordinate invasive pressure monitoring and procedures early, especially if considering advanced ARDS management techniques and/or evidence of impending distributive shock.
- Under sterile technique, establish central access early in anticipation of the need for continuous vasopressors.
- Multiple peripheral IVs likely needed for infusions of sedatives, analgesia, antibiotics.
- A conventional central venous catheter can be placed through an introducer catheter (i.e. Cordis) to increase number of infusion ports during the initial insertion.
- Excessive fluid resuscitation likely harmful, careful assessment of volume responsiveness required. If available, patient stable not on vasopressors, and evacuation is significantly delayed, may use loop diuretics to gain net-even volume.
- ∎Development of arrhythmias and dilated cardiomyopathy with cardiogenic shock may develop in severely ill COVID-19 patients due to systemic inflammation, stress, or a direct viral myocarditis requiring vasopressors. Manage arrhythmias as per ACLS guidelines.
- Unexpected change in vital signs trends or hypotension out of proportion to sedation and PEEP indicates shock. Development of jugular venous distension and cool mottled extremities may indicate cardiogenic shock. Limited transthoracic echocardiography may be useful to determine shock cause.
- Utilize measures of volume responsiveness (urine output, pulse pressure variation, and blood pressure response to passive straight leg raise) to help guide the need for further fluid resuscitation. Note: An increase of EtCO2 of >5% OR 3mmHg after passively raising a patient’s legs up 45 degrees from a fully supine position suggests volume responsiveness.
- Norepinephrine is first line vasopressor for shock. Vasopressors should be titrated to a MAP goal of greater than or equal to 65mmHg.
Medication Administration
Consider systemic corticosteroids in the treatment of COVID-19 related moderate to severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS). Discuss with advanced provider via telehealth prior to initiating treatment.
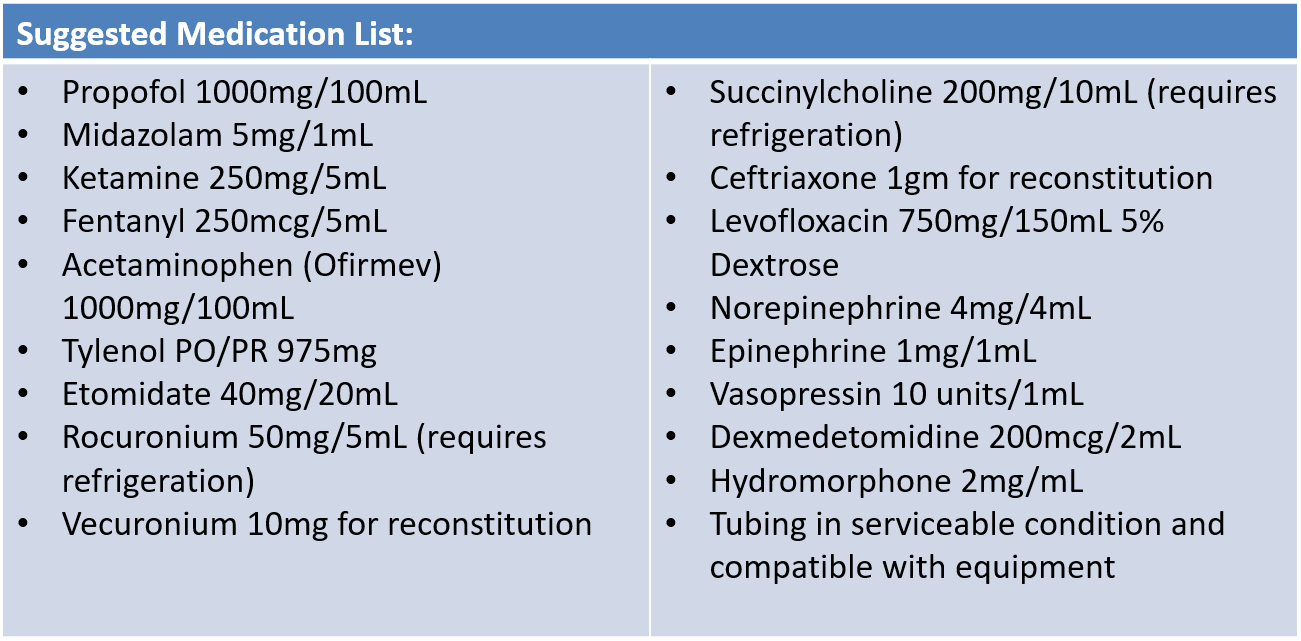
- Consider early azithromycin (oral or IV 500mg daily for a minimum of 5 days) for community acquired pneumonia (CAP) for those with lower respiratory tract symptoms and fever. Use azithromycin with caution due to potential arrhythmias, particularly in older patients or those with known cardiac problems. Monitor QTc interval if possible.
- For severe symptoms, add ceftriaxone (IV 2gm q24h is the best option) or ampicillin-sulbactam (IV 3gm q6hr is a better option) or ertapenem (IV 1g q24h is a good option). If critically ill, include levofloxacin (IV 750mg q24h) to treat of bacterial co-infection.
- Due to potential harm, prior to starting chloroquine (CQ) or hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) plus azithromycin, discuss with advanced provider via telehealth.
- If azithromycin not available, may substitute doxycycline (IV or PO 100mg q12h) to treat bacterial pneumonia.
IV acetaminophen 1000mg every 6 hours (or PO/PR 975mg every 6 hours) as needed for temperature over 38degC (100.4 degF)
- Sedation goal is Richmond Agitated Sedation Scale (RASS -1 to -2 comfortable, transiently responsive to verbal stimulation) and synchronous with the ventilator. Increase sedation and/or add narcotics to improve patient-ventilator synchrony. Use of paralytics is likely to be required for very severe cases.
- Ketamine may cause increased secretions requiring more frequent suctioning. If in-line close-circuit suction devices are not available, patients may not tolerate the de-recruitment caused by disconnecting the ventilator for suctioning. This will also increase aerosolization risk. For limited medication availability, consider midazolam administration more frequently to decrease Ketamine dose requirement & secretion burden.
- Combined use of multiple sedatives (i.e. propofol, dexmedetomidine, and/or midazolam) may decrease total sedative requirement, mitigating the hypotensive effects of propofol. Use caution in combining propofol and dexmedetomidine, especially in younger patients, leading to bradycardia & hypotension.
- Intermittent or continuous infusions of fentanyl or intermittent hydromorphone (if available) may be used for analgesia & ventilator synchronization.
- Low dose vasopressors may be necessary to maintain blood pressure with administration of deep sedation & higher PEEP
- Adequate depth of sedation is essential prior to starting paralytic; recommend at least RASS -3.
- Recommend intermittent paralytics over continuous infusions if possible.
- Bolus (for push-dose or for loading dose of an infusion): IV 5mg to 10mg every 60-90 minutes as needed.
- Infusion: 0.8 to 1.2mcg/kg/min (approx. 80mcg/min for 80kg).
- Without pump: 40mg vecuronium in 250mL bag of normal saline yields 40mg/290mL = 138mcg/mL. For 80mcg/min = 0.58mL/min ~ 1gtt every 10 seconds in 10gtt tubing.
- Use metered-dose-inhalers (MDIs) over nebulized bronchodilators to minimize aerosolization.
- If the ventilator tubing does not have a capped inlet for medication administration (aka MDI adapter): clamp the ETT, disconnect the ventilator, and administer the MDI (6 puffs) directly into the INHALATION circuit. Then, reconnect the ventilator and unclamp ETT to insufflate the medication.
- Magnesium Sulfate 2gm IV over 20 minutes (similar to asthma exacerbation treatment) may be safer to treat of bronchospasm due to aerosolization risk from circuit disconnection.
Fixed rate vasopressin infusion (0.04 units/min) is useful as an early adjunct in non-cardiogenic shock; may start vasopressin when norepinephrine reaches doses above 12mcg/min. Epinephrine is the second line titratable pressor.
Diagnostics
- If a patient has known risk for or exposure to COVID-19, manage as a PUI regardless of the differential diagnosis.
- Examination should include, but not limited to, full vital signs including pulse oximetry, work of breathing assessment, pulmonary auscultation, skin temperature, and capillary refill.
- COVID-19 RT-PCR assay not usually available in austere environments.
- Co-infections along with alternative and/or comorbid diagnoses are possible.
- Life threatening alternative diagnoses (e.g. pulmonary embolism, pneumothorax, acute myocardial infarction, etc.) should be considered and managed according to standard practices.
- False negative rates for COVID-19 RT-PCR assay tests are significant. Isolate & treat (or quarantine) those with typical symptoms, recent travel and/or exposure to another sick individual.
- Testing priority should be guided by CDC recommendations balanced with operational priorities. Mild symptoms and no high-risk factors may not warrant immediate testing, while mission critical is determined by the combat command, and testing may be considered a higher priority.
- If testing is negative, release from strict isolation while following strict social distancing practices, wearing a face covering, and thoroughly cleaning their workplace.
Minimum:
- If febrile and in malaria endemic area: Binax Now rapid malaria testing
Better (Above +):
- Ultrasound (pulmonary + cardiac)
- If dyspnea/hypoxia - iStat ABG or VBG
- 12-Lead ECG
- Rapid Flu Testing
- Rapid Dengue Testing
Best (Above +):
- Chest X-Ray
- Respiratory Pathogen Film Array (i.e. Biofire)
- COVID-19 PCR Testing
- Other laboratory testing listed DoD COVID19 PRACTICE MANAGEMENT GUIDE
- Among patients with mild symptoms & normal resting SpO2, risk of deterioration is increased in those presenting with dyspnea (even if mild), desaturation on exercise testing, & those with comorbidity (age over 45, cardiovascular disease, pulmonary disease). These patients should be monitored closer & considered for evacuation sooner.
- Exercise Test: Patient should jog or walk in place for 3 minutes. Inability to complete the test or desaturation below SpO2 <94% confers a higher risk for clinical deterioration. This is an un-validated triage test used by hospitals to help gauge the need for closer inpatient monitoring.
- If a patient has known risk for or exposure to COVID-19, the patient should be managed as a PUI regardless of the differential diagnosis. COVID-19 patients can be co-infected with other pathogens or possess other underlying conditions.
- Life threatening alternative diagnoses (e.g. pulmonary embolism, pneumothorax, acute myocardial infarction, etc.) should always be considered and managed according to standard practices for diagnosis and treatment.
Coagulopathy with mild thrombocytopenia, increased D-dimer levels (strongly associated with greater risk of death), increased fibrin degradation products, and prolonged prothrombin time
Nursing Care & Monitoring
- Rapid decompensation may occur 5-7 days out from onset of symptoms, and ARDS onset within 12 to 48hrs following initial signs of clinical deterioration. Close monitoring during this period is critically important to allow for early intervention.
- Always keep clamp at head of bed for clamping ET tube if ventilator disconnected.
- Periodic prone positioning and percussive chest physiotherapy, if tolerated, may improve secretion clearance.
- Ventilator patients placed in reverse Trendelenberg positioning (head of bed up, spine straight) improve breathing. Avoid semi-recumbent position (bent at the waist) which impedes breathing
- Strongly recommend IV pump over dial-a-flow over drip-chamber titration due requirement to continually monitor/adjust titration.
- Establish invasive procedures & pressure monitoring early, especially if considering advanced ARDS management techniques and/or evidence of impending distributive shock.
- Development of arrhythmias & dilated cardiomyopathy with cardiogenic shock may develop in severely ill COVID-19 patients due to systemic inflammation, stress, or a direct viral myocarditis and may require vasopressors. Manage arrhythmias as per ACLS guidelines.
- Measures of volume responsiveness (urine output, pulse pressure variation, and blood pressure response to passive straight leg raise) guides need for further fluid resuscitation. Note: An increase of EtCO2 of >5% OR 3mmHg after passively raising a patient’s legs up 45 degrees from a fully supine position suggests volume responsiveness.
Note: Hypotension out of proportion to sedation and PEEP indicates further need of evaluation into causes of shock. Development of jugular venous distension and cool mottled extremities may indicate cardiogenic shock. Limited transthoracic echocardiography may be useful in discriminating between hypovolemic, cardiogenic, & distributive shock (in personnel trained to perform the assessment).
- Anticipate ventilator patient complications such as pneumothorax. Sudden increases in PIP and/or hemodynamic instability suggest pneumothorax.
- Pneumomediastinum with subcutaneous emphysema may develop with high PEEP. Look for crepitus across the chest, neck, and/or upper extremities. Tension physiology from pneumomediastinum is rare.
- If oliguria does not improve with resuscitation, consider acute tubular necrosis (ATN), especially if UOP remains low for more than 6 hours.
- If iStat creatinine testing for acute kidney injury (AKI) not available, use urine dipstick testing for specific gravity, proteinuria, and hematuria.
- Abnormally low (dilute) specific gravity in the setting of oliguria suggests tubular damage and the inability to concentrate urine.
- Significant proteinuria can be seen in acute tubal necrosis (ATN), but may not be specific.
- Hematuria may suggest the presence of myoglobinuria – consider rhabdomyolysis as cause of acute kidney injury (AKI).
- If urinary output (UOP) suddenly declines or stops, flush Foley/perform a bladder ultrasound to determine mechanical (Foley blockage) vs. organic (true kidney disease) cause.
- If ATN suspected, DO NOT AGGRESSIVELY FLUID RESUSCITATE OR DIURESE to meet UOP goals. Use alternate markers of fluid responsiveness (blood pressure response to passive straight leg raise) to help determine the need for further fluids and vasopressors.
- Monitor electrolyte closely for disturbances, specifically metabolic acidosis and hyperkalemia. Diuresis for management of hyperkalemia may be appropriate but should be done after teleconsultation.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) often begin in the vessels of legs or arms, leading to fatal outcomes by traveling to the heart (myocardial infarction), brain (stroke), and/or lungs (pulmonary embolism).
- Monitor for signs or symptoms of DVT including pain or tenderness, swelling, increased warmth in the affected area, and redness or discoloration of the overlying skin.
- Monitor for the most common signs or symptoms of pulmonary embolism including unexplained shortness of breath, pleuritic chest pain, cough or hemoptysis, and syncope.
- Provide thromboembolism prevention measures including calf muscle exercises, range-of-motion, properly fitted compression stockings if available.
- Absence of muscle movement and no evidence of spontaneous breathing on the ventilator. If possible, titrate to 2/4 train-of-four (TOF) score (likely only available for surgical teams).
- Increased HR and BP may suggest undersedation and should be empirically treated with an increased dose of sedation.
- Recommend checking TOF every 2-4 hours until stable, then consider extending to every 6-8 hours.
- Once the patient is stabilized, consider holding the paralytic at least once every 24 hours to provide for assessment of sedation depth.
- DO NOT hold sedation until 4/4 TOF twitches, unless absolutely necessary (e.g. sudden hypotension). Alternatively, spontaneous respiratory efforts (respiratory rates higher than the set rate) can be used as evidence of adequate paralytic medication reversal.
- NG/OGT should be placed early for gastric decompression. If medical evacuation is significantly delayed (greater than 24 hours), consider starting enteral nutrition.
- Enteral nutrition is contraindicated in hemodynamically unstable patients (i.e. those on high or increasing doses of vasopressors). Low volume enteral feeding on patients with stable low doses of vasopressors is generally safe.
- At a minimum, confirm presence of gastric placement with auscultation over both lung fields and the abdomen along with aspiration of gastric contents. Urinalysis test strips for pH may provide an addition method for field expedient NG/OGT placement confirmation in patients not on acid suppressive therapy.
- Ensure presence of normal bowel sounds prior to initiating any enteral feeding. Enteral feeding contraindicated in the presence of signs of acute abdomen and/or gastro-intestinal bleeding.
- Goal 25-30kcal/kg/day + 1-1.2gm/kg protein; however, this might be difficult, especially in the absence of formal concentrated tube feeds.
- Hypocaloric feeding is acceptable if accompanied by adequate protein supplementation.
- Meal supplement drinks are not sufficient. For example, 1x Muscle Milk Light bottle contains only 150kcal and 28gm protein in 500mL, more diluted than most tube feeding formulations. This may cause increased extra-vascular lung water and minimal benefit for those critically ill.
- Use commercially available protein powder (with similar caloric/protein content per scoop) at 1/4 the recommended concentration and mix in a blender until no clumps are visible. Administer in small volume boluses (e.g. 60mL via Toomey syringe) as tolerated every 2 to 4 hours to a goal of 1gm/kg/day protein content.
Prevent & Control Infection
Contact: Spreads via direct contact with an infected patient or contaminated surface. Contact precautions reduce method of transmission.
Note: Covid-19 may survive on surfaces for 96 hours or longer. Decontaminate surfaces frequently using a diluted bleach solution by mixing 5 tablespoons (1/3 cup) bleach per gallon of water. Clean and disinfect high-touch surfaces frequently medical such as equipment, floors, tables, hard-backed chairs, doorknobs, light switches, phones, tablets, touch screens, keyboards, handles, desks, toilets, sinks. If a separate, designated bathroom is not available, bathrooms should be cleaned and disinfected after each use by personnel wearing best possible PPE, and waste considered hazardous, disposed according to theater hazardous waste policy.
Droplet: Spreads via relatively large liquid particles that settle from the air quickly (within a few feet). Droplet precautions reduce transmission.
Airborne: Spreads of via small liquid particles (aerosols) that remain suspended in the air for prolonged periods of time, traveling longer distances. Airborne precautions reduce transmission.
- Wash hands with warm, soapy water (for at least 20 seconds), or use alcohol hand sanitizer (allowing to dry) before and after patient care, after touching PPE, especially facemask, goggles.
- Healthcare personnel should use best available PPE and remove PPE with assistant when available to avoid cross contamination
- Decontaminate goggles, glasses, face shield with diluted bleach solution between uses
- Place the monitor, ventilator, and IV pumps upwind and as far away as possible from the patient to minimize exposure to medical personnel.
- For chest tube management, water seal closed chest drainage system preferable over dry seal/Heimlich valve due to aerosolization.
- Sputum specimen obtained via cough, nasal or orotracheal suction, tracheal intubation, tracheal extubation (accidental or planned)
- Bag-valve mask ventilation, ventilator circuit disconnection, non in-line tracheal suctioning, tracheostomy, cricothyroidotomy, cardiopulmonary resuscitation (before intubation and connection to ventilator circuit)
- Surgical procedures involving the face, neck, or thorax
- Minimum: face covering, eye protection glasses, gloves, and makeshift gown. Note: for patients with low probability of disease and where direct contact with the patient, their secretions, or other bodily fluids is low, gowns may not be required (mirroring conventional droplet precautions).
- Routine Care: surgical mask or N95 mask, face shield (either standalone or with mask) and eye protection, gloves, gown (surgical or contact), head covering.
- N95 mask (with or without surgical mask covering) with face shield or hood/face shield (e.g. CBRNE pro-mask) along with gown and gloves. Disposable head covering is also highly recommended.
- Eye protection glasses and face shields should be cleaned with a diluted bleach solution between uses.
- NIOSH recommends the following for extended use and re-use of N95 respirators:
- N95 masks should be discarded following aerosol generating procedures (e.g. intubation) or when visibly contaminated with bodily fluids.
- Consider using a large face shield that sits in front of the mask, wear a surgical mask over-top of the N95, and masking the patient to minimize contamination.
Plan & Conduct Evacuation
- May take more than 24 hours to execute an evacuation mission.
- Initiate evacuation coordination for PUI patients, regardless of symptoms, to next level of care as soon as possible due to limited oxygen supply, lack of advanced critical care capabilities, and limited number and availability of evacuation platforms.
- Patient Movement should be anticipated for COVID-19 PUIs when symptoms present concerning for progression of disease. There is no reason to delay request for evacuation.
- Ground and Air Medical Transport will depend on local CASEVAC/MEDEVAC notification plan and CASEVAC/MEDEVAC platforms available for transport.
- When clinically & operationally feasible, within the provider’s scope of practice, obtain central venous access in anticipation of need for multiple infusions, including vasopressors. Obtain at least two peripheral IV’s or one peripheral plus one central line access prior to transport, if possible.
- Early placement of arterial access secured by suture for invasive pressure monitoring is recommended, if available.
- Due to probability of myocardial injury, obtain ECG and troponin, if possible. Coordinate the medical management of acute coronary syndrome or myocarditis via teleconsultation prior to transport, if possible.
- Patients requiring >3 Lpm oxygen support to maintain oxygen saturations >92% may not tolerate the hypoxic environment of aeromedical evacuation and require pre-flight intubation.
- Consider consulting the Advanced Critical Care Evacuation Team (ACCET) DSN 312-429-BURN (2876) before transporting patients on moderate to high ventilator settings (PEEP > 14 and FiO2 > 70%). Refer to JTS Acute Respiratory Failure CPG. If prone ventilation is to be utilized in-flight, position patient pre-flight with adequate time to document patient stability and an arterial blood gas before transport. Review prone positioning procedures in the JTS Acute Respiratory Failure
- If intubated, place NG/OGT pre-flight and attached to intermittent suction. Post-pyloric enteric feeds may be continued in-flight using small bolus sizes (30 cc) and given twice hourly.
- Assemble and send pre-drawn and pre-mixed medications with primed tubing prior to transport.
- Prepare patient records for handoff including medical notes, ECGs, laboratory results, and imaging results (if available).
- Prepare patient belongings and ID/passport to accompany the patient.
- Place PPE for flight on patient including eye protection and ear protection, and DO NOT forget casualty face covering if not intubated.
- Early patient report allows the evacuation team to prepare any medications and equipment that cannot be provided by the sending facility.
- Sending facility medical team should provide contact information when requesting patient movement.
- Evacuation team should contact the Role 1-2 medical team for initial report via approved means.
- Provide up-to-date COVID-19 status (PUI vs confirmed)
- Current vital signs, exam findings, and recent trends or changes
- Current medication regimen if initiated (including antibiotics and anticoagulants)
- Critical care medication regimen (sedation, analgesia, paralysis, and vasopressors)
- Current PPE status, oxygen requirements and ventilator settings
- Any potential COVID-19 related complications identified during management (e.g. heavy respiratory secretions)
Note: Upon evacuation team arrival to receive the patient, handoff report should be repeated with key elements above, including any recent patient changes.
Warning: Transition to the evacuation team equipment presents risk of exposure to healthcare team. To reduce risk: Personnel should be limited to those directly involved in the care of the patient. Best available PPE should be worn by everyone involved in the care transition.
- ETT clamping technique should be instituted to limit aerosol creation during all ventilator circuit breaks including transfer to evacuation team ventilator
- Sufficient time should be allotted to confirm adequate oxygenation and ventilation prior to departure of the evacuation team.
Documentation
Use COVID-19 H&P and associated forms. Document COVID-19 status (PUI vs confirmed), vital signs, exam findings, and monitoring trends or changes, medication regimen including antibiotics, anticoagulants, sedation, analgesia, paralysis, and vasopressors), PPE status, oxygen requirements, and ventilator settings
Manage Equipment
Equipment must be decontaminated before sharing between patients & according to manufacturer recommendations.
- Use cloth face covering when risk is low to conserve supply of surgical face masks and N95 masks needed for high risk procedures.
- Remove PPE in a manner that allows for it to be easily worn again without contacting contaminated surfaces.
- N95 maintain their effectiveness for at least 8h of continuous or intermittent use.
- To re-use surgical face masks or N95 masks: while wearing gloves, store the mask in a bag in a dry, shaded/indoor area for 72h prior to using again. DO NOT use bleach or UV radiation (i.e. sunlight) to ‘sterilize’ the N95 – this will degrade mask effectiveness.