Prehospital Blood Transfusion
Joint Trauma System
PREHOSPITAL BLOOD TRANSFUSION
Rapid Update, Jun 2023: Calcium administration changed to 1 gram calcium
Purpose
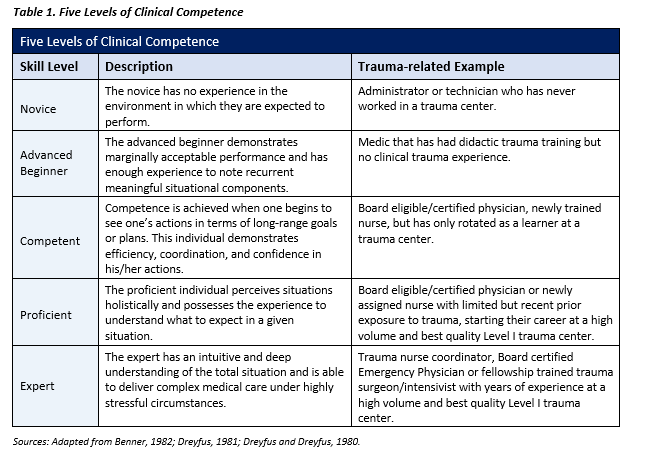
This Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) provides a brief summary of the scientific literature for prehospital blood use, with an emphasis on the en route care environment. Updates include the importance of calcium administration to counteract the deleterious effects of hypocalcemia, minimal to no use of crystalloid, and stresses the importance of involved and educated en route care medical directors alongside at a competent prehospital and en route care providers (See Table 1.) With the paradigm shift to use FDA-approved cold stored low titer group O whole blood (CS-LTOWB) along with the operational need for continued use of walking blood banks (WBB) and point of injury (POI) transfusion, there must be focused, deliberate training incorporating the different whole blood options. Appropriate supervision of autologous blood transfusion training is important for execution of this task in support of deployed combat operations as well as other operations in which traumatic injuries will occur. Command emphasis on the importance of this effort as well as appropriate logistical support are essential elements of a prehospital blood program as part of a prehospital/en route combat casualty care system.
INTRODUCTION
Early administration of blood products to the trauma patient in extremis is the standard in combat casualty care and becoming more common as part of a strategy of civilian prehospital critical care.1-7 Although there is some dissent regarding the level of evidence for and benefits of prehospital blood transfusion in the civilian literature, much of the data informing that discussion precedes the use of whole blood and involves a patient population dissimilar from the military.8,9 Civilian Emergency Medical Services systems internationally10,11 and in Texas, North Carolina and several other states have initiated whole blood transfusions in the prehospital environment. At least one civilian tactical law enforcement team has initiated a Low-Titer O Fresh Whole Blood program.12 The main military literature covering this topic is summarized in Table 2 below.
PREHOSPITAL PRINCIPLES OF RESUSCITATION AND TRANSFUSION
- Rapid recognition of life-threatening hemorrhagic shock
- Point of care devices if available: international normalized ratio; lactate level may be of value.
- Prevent hypothermia
- Hemorrhage control with mechanical hemostatic adjuncts:
- Tourniquet/junctional tourniquet
- Pressure dressings/thrombin and fibrin impregnated gauze
- Hemostatic Resuscitation
- Whole blood (WB) is optimal
- FDA approved CS-LTOWB
- Low titer group O whole blood (LTOWB)
- Type O-WB (non-titered)
- Component therapy with plasma (dried, liquid, or, thawed), red blood cells (RBCs), and platelets in 1:1:1 ratio
- Whole blood (WB) is optimal
- Avoid hypocalcemia/Calcium replacement
- In prolonged evacuations, empiric calcium administration for every 4-6 units of RBCs or WB
- Avoid crystalloid resuscitation
- Tranexamic Acid administration if less than 3 hours from time of injury
- Consider source of Freeze Dried Plasma if available
NOTE: Conventional goal is systolic blood pressure >90mmhg. Recent concept indicates a higher goal of 90-110mmHg due to shift towards blood-based resuscitation and concern for prolonged hypoperfusion especially for patients with long transport times.
CRITERIA FOR TRANSFUSION
Prehospital blood transfusion is predicated upon clearly defined criteria for the use of this valuable resource. Several high performing military and civilian prehospital medical teams use prehospital blood transfusion according to protocolized guidelines. The U.S. Army Ranger Regiment was an early adopter of prehospital blood transfusion and uses the following criteria for transfusion: signs and symptoms of hemorrhagic shock; OR 1+ amputation; blunt/penetrating trauma (junctional/abdominal/thoracic); OR pelvic fracture; OR SBP <100; OR lactate >5; pulse >100.20 In Australia, the Greater Sydney Area Helicopter Emergency Medical Services (GSA-HEMS) is an intensivist-based prehospital critical care service that has extensive experience in prehospital blood transfusion. In the prehospital environment, they transfuse blood if there is “persistent hemorrhagic shock despite hemorrhage control measures after crystalloid infusion.”21 During interhospital transport GSA-HEMS transfuses blood if there is “persistent hemorrhagic shock where there is limited or no access to cross-matched blood and [an] ongoing requirement for transfusion.” The Australian Queensland Ambulance Service Trauma Response Team administers blood products in the prehospital environment and a retrospective review of cases was published in 2014 demonstrating benefit in appropriate clinical situations.22 In 2014, proposed criteria for prehospital blood products in combat casualties were refined based on data from Afghanistan23 and updated in 2020 using a larger data set from the entire DoD Trauma Registry (DoDTR).24 A case series reviewing the benefits of early whole blood administration in combat casualties was published in 2016.25
Development of transfusion criteria is an important consideration in establishment of a prehospital transfusion program. In the civilian trauma center experience, 596 trauma patients were evaluated using an assessment of blood consumption (ABC) score.26 Patients received one point for any of the following: penetrating mechanism; positive focused assessment sonography for trauma (FAST); systolic blood pressure less than 90 mmHg; heart rate greater than or equal to 120 beats per minute. An ABC score of two or greater predicted the need for massive blood transfusion with 75% sensitivity and 86% specificity. This investigation demonstrated the utility of a quick, non-laboratory based tool to predict the need for blood transfusion.
Careful attention to transfusion triggers can limit wastage of this important resource in a potentially resource constrained environment. Furthermore, it is important to note that blood product usage can be optimized when hemorrhage control is undertaken simultaneously.5,7 Ensure that hemorrhage control efforts are properly employed in accordance with Tactical Combat Casualty Care Guidelines. When administering blood, be certain to alert the receiving facility that the patient is requiring blood transfusion, noting any potential need for massive transfusion.
PROCEDURE
Certain special considerations for blood transfusion have been enacted in other Department of Defense transfusion algorithms.27 Rapid transfusion of blood can cause sheering of RBCs and should be avoided if possible. When possible, low titer group O whole blood (LTOWB) should be administered as the blood product of choice. LTOWB has been screened for Anti-A and Anti-B antibodies. The titer of these antibodies is low enough to represent minimal risk of clinical consequences, and may be considered a universal donor. LTOWB will be exclusively drawn from sites approved by the Armed Services Blood Program (ASBP), distributed in theater via the ASBP blood distribution system and fully tested in accordance with FDA guidelines.
Blood products should be transfused in a plasma:platelet:RBC ratio of 1:1:1. If platelets are not available, then plasma:RBC should be transfused in a 1:1 ratio. If that is not possible, then reconstituted dried plasma, liquid plasma or thawed plasma alone or RBCs alone should be transfused.
If available, type O negative RBCs should be used preferentially for females of childbearing years. If it is necessary to administer O positive blood to a woman of childbearing years with O negative blood, then consider Rhogam therapy to decrease the risk to subsequent pregnancies. Please note though that resuscitation and prevention of exsanguination takes precedence of potential future pregnancy complications. Pediatric blood transfusion should be based on clinical signs of shock rather than predefined vital signs, since vital signs can vary considerably between age groups in pediatric patients.
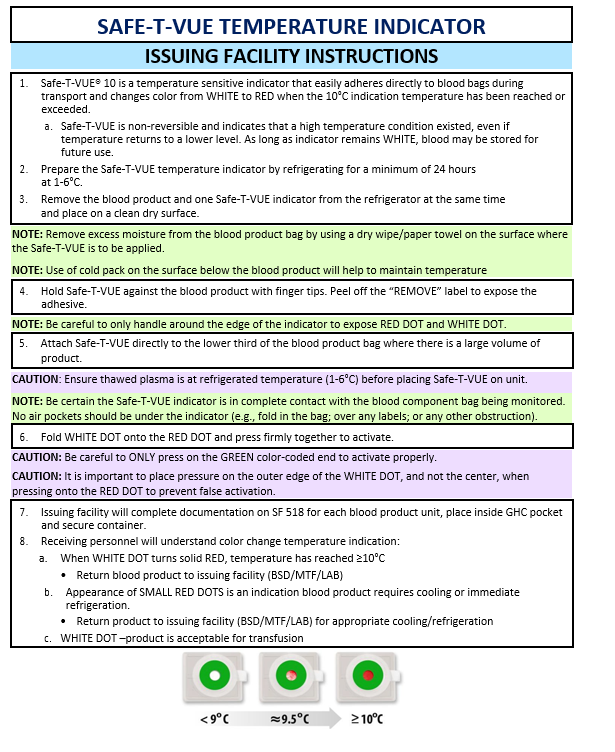
Blood plasma contains important clotting factors and can be transfused rapidly. Thawed plasma has a shelf life of 5 days and may not be available for prehospital missions. “Never frozen” liquid plasma has a shelf life of 26 days and may be more readily available. Check with the issuing facility for availability of thawed or liquid (i.e. never frozen) plasma. All blood products must be transfused immediately after removal from the storage container. If transfusion is delayed, then blood products that have been removed from storage and exceeded proper temperature will be returned to the issuing facility per local policy. Ensure that all blood products issues have a Safe-T-VUE (NSN 6515-08-T00-3056) attached and activated for temperature monitoring. (See Appendix E).
QUALITY CONTROL
Proper storage, transport and administration of blood and blood products is addressed the following Joint Trauma System CPGs: Damage Control Resuscitation,28 Frozen and Deglycerolized Red Blood Cells29 and Whole Blood Transfusions.30
Ensure that the blood product container (NSN 6530-01-505-530I; OCP/5306; Desert) is properly charged and maintained prior to loading blood products. Ensure that all blood products have a Safe-T-VUE attached and activated for temperature monitoring. Ensure that thawed plasma is at a refrigerated temperature (1-6 degrees C) prior to placement of Safe-T-VUE. Appropriately document issuance and use of blood products per local protocol, including documentation in Theater Medical Data Store (TMDS) inventory.
Blood products carried outside of a medical treatment facility (MTF) and/or laboratory will be contained in an approved storage container for a maximum of 48 hours. Once loaded and sealed, a container will remain closed and intact until used for patient care or returned to the issuing facility. Units will inspect blood product containers and document appropriate quality metrics (e.g., intact, no leaking) every 24 hours.
TRANSFUSION REACTION
The rate of non-infectious transfusion reaction is low.31 In a recent evaluation of 4,857 transfusion episodes approximately 1% were associated with a serious reaction.32 Transfusion-associated circulatory overload was most common (~1%); while transfusion-related acute lung injury, anaphylactic reaction and hypotensive reactions all occurred in less than 0.1% of transfusions. Other investigators evaluated emergency transfusion of 5,203 units of type-O RBC to 480 trauma patients and found that no acute hemolytic transfusion reactions occurred.33
In the unlikely event of a prehospital transfusion reaction, immediately stop the transfusion. In cases of anaphylaxis, administer 0.3 mL of 1:1000 epinephrine intramuscularly (IM), administer diphenhydramine 25 mg IV or IM and consider methylprednisolone (the FDA approved dose of methylprednisolone is 10 – 40 mg IV over several minutes, with subsequent doses being determined by clinical response). Maintain the patient’s airway as needed and administer IV fluids in cases of hypotension. In cases of acute hemolytic reaction, administer diphenhydramine 25 mg IV or IM, and consider osmotic diuresis with mannitol 20% 20 gm or 3% sodium chloride 250 mL.
HYPOCALCEMIA
Calcium administration should be considered in all patients undergoing en route care blood transfusion. The citrate preservative in blood products can chelate calcium and contribute to hypotension in patients who have received blood products.34 In 352 patients who were critically bleeding and required massive transfusion, investigators found that hypocalcemia worsened mortality. Patients generally had low ionized calcium concentration (mean = 0.88mmol/L) and had higher odds of mortality (Odds Ratio = 1.25, 95% Confidence Interval 1.04-1.52; P = 0.02). Admission hypocalcemia is further associated with mortality.35 Calcium concentration was measured in 591 trauma patients before administration of blood products. Those with an ionized calcium < 1 experienced higher mortality (15.5%) compared to those with ionized calcium levels >1 (mortality = 8.7%, p = 0.036).
Trauma patients are often hypocalcemic without regard to transfusion status, further suggesting that calcium administration may be beneficial.36,37 In 212 trauma patients with a mean Injury Severity Score (ISS) of 34; 64% were found to be hypocalcemic (with calcium < 1.15 mmol/L) and 10% were severely hypocalcemic (<0.9mml/L). Hypocalcemia is common in massive transfusion and associated with increased mortality.38,39 Although the mechanism of this effect is not completely understood, it is thought that acidemia related to tissue hypoperfusion may play a role.40 Administration of one gram of calcium IV/IO before, during (using a secondary access point) or immediately after the first unit of blood product. Re-dose one gram of calcium IV/IO after every 4 units of blood products.
TRAINING
Execution of prehospital and en route care blood transfusions requires sufficient training to adequately prepare. Conducting the most realistic training possible has been shown to improve in-hospital trauma team performance as well as the widely held belief of military training in general. Whole blood training should be viewed similarly.41 Coordinated and deliberate autologous blood labs with appropriate oversight can safely achieve the highest degree of realism with relatively low cost.42,43 Armed services blood bank policies for donor allowance in autologous blood lab participants is still under discussion.
PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT (PI) MONITORING
Population of Interest
- All patients who receive blood product transfusion within 3 hours of injury
- All patients who meet criteria for blood transfusion (severe traumatic injury: ISS ≥16 and ≥ 2 body regions injured with AIS severity ≥ 2 AND SBP < 100 OR HR > 100 OR hematocrit < 32% OR pH <7.25) within 3 hours of injury
Intent (Outcome)
- LTOWB is used for prehospital resuscitation of casualties with life-threatening injuries and hemodynamic instability (HR > 100 or SBP < 100).
- For the population of interest, the first resuscitation fluid given after injury is a blood product, ideally cold-stored LTOWB.
- Administration of whole blood and blood products to appropriate combat casualties in the prehospital and en route care environment.
Performance/Adherence Metrics
- The number and percentage of patients in the population of interest who receive WB transfusion prior to arrival at first role of care.
- Number and percentage of patients in population of interest who received a blood product as the first resuscitation fluid.
- Number and percentage of patients in population of interest who received cold-stored LTOWB as the first resuscitation fluid.
- Indication identified.
- Pre and post vital signs measured.
- Calcium administration documented.
- Appropriate information collected for donor and recipient exposure monitoring.
DATA SOURCES
- Patient Record (DD1380/DA4700 OP7)
- DoDTR
SYSTEM REPORTING & FREQUENCY
The above constitutes the minimum criteria for PI monitoring of this CPG. System reporting frequency will be performed annually; additional PI monitoring and system reporting may be performed as needed.
The system review and data analysis will be performed by the JTS Chief and the JTS PI Improvement Branch.
Responsibilities
It is the Unit Medical Director’s responsibility to ensure familiarity, training, appropriate compliance and PI monitoring at the local level with this CPG. Coordination with the Regional Medical Director and Trauma Director is also essential in ensuring full spectrum compliance and PI monitoring along with clear communication with the Combatant Command Trauma System and Joint Trauma System.
REFERENCES
- Donham BP, Barbee GA, Deaton TG et al. Risk associated with autologous fresh whole blood training. J Spec Oper Med.. 2019;19(3);24-25.
- Butler FK, Holcomb JB, Schreiber MA, Kotwal RS, Jenkins DA, Champion HR et al. Fluid Resuscitation for Hemorrhagic Shock in Tactical Combat Casualty Care: TCCC Guidelines Change 14-01--2 June 2014. J Spec Oper Med. 2014;14(3):13-38.
- Strandenes G, Hervig TA, Bjerkvig CK, et al. The lost art of whole blood transfusion in austere environments. Curr sports med rep. 2015;14(2):129-34.
- Cap AP, Pidcoke HF, DePasquale M, et al. Blood far forward: Time to get moving! J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015;78(6 Suppl 1):S2-6.
- Fisher AD, Miles EA, Cap AP, Strandenes G, Kane SF. Tactical damage control resuscitation. Mil med. 2015;180(8):869-75.
- Butler FK, Jr. Fluid resuscitation in tactical combat casualty care: yesterday and today. Wilderness Environ med. 2017;28(2S):S74-S81.
- Chang R, Eastridge BJ, Holcomb JB. Remote damage control resuscitation in austere environments. Wilderness environ med. 2017;28(2S):S124-S34.
- Smith IM, James RH, Dretzke J, Midwinter MJ. Prehospital blood product resuscitation for trauma: a systematic review. Shock (Augusta, Ga.). 2016 Jul;46(1):3.
- Shand S, Curtis K, Dinh M, Burns B. What is the impact of prehospital blood product administration for patients with catastrophic haemorrhage: an integrative review. Injury. 2019 Feb 1;50(2):226-34.
- Yazer MH, Spinella PC. An international survey on the use of low titer group O whole blood for the resuscitation of civilian trauma patients in 2020. Transfusion. 2020;60:S176-179.
- Nadler R, Tsur A, Yazer MH et al. Early experience with transfusing low titer group O whole blood in the pre-hospital setting in Israel. 2020;60:S10-S16.
- Fisher AD, Dunn J, Pickett JR et al. Implementation of a low titer group O whole blood program for a law enforcement team. Transfusion. 2020;60:S36-S44.
- Powell-Dunford N, Quesada JF, Gross KR, Shackelford SA. Army Air Ambulance Blood Product Program in the combat zone and challenges to best practices. Aerospace med hum perform. 2016;87 (8):728-34.
- Malsby RF, 3rd, Quesada J, Powell-Dunford N, et al. Prehospital blood product transfusion by U.S. army MEDEVAC during combat operations in Afghanistan: a process improvement initiative. Mil med. 2013;178(7):785-91.
- Mabry RL, Apodaca A, Penrod J, Orman JA, Gerhardt RT, Dorlac WC. Impact of critical care-trained flight paramedics on casualty survival during helicopter evacuation in the current war in Afghanistan. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;73 (2 Suppl 1):S32-7.
- Morrison JJ, Oh J, DuBose JJ, et al. En-route care capability from point of injury impacts mortality after severe wartime injury. Ann surg. 2013;257 (2):330-4.
- Apodaca A, Olson CM, Jr., Bailey J, et al. Performance improvement evaluation of forward aeromedical evacuation platforms in Operation Enduring Freedom. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013;75 (2 Suppl 2):S157-63.
- Shackelford SA, Del Junco DJ, Powell-Dunford N, et al. Association of prehospital blood product transfusion during medical evacuation of combat casualties in Afghanistan with acute and 30-day survival. JAMA. 2017;318 (16):1581-91.
- O'Reilly DJ, Morrison JJ, Jansen JO, et al. Prehospital blood transfusion in the en route management of severe combat trauma: a matched cohort study. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014;77 (3 Suppl 2):S114-20.
- Donovan W. Ranger Medic Handbook. 4th ed. North American Rescue 2012.
- Reid C. Blood Management. In: Greater Sydney Area Helicopter Emergency Medical Service. Sydney. 2015.
- Bodnar D, Rashford S, Hurn C, et al. Characteristics and outcomes of patients administered blood in the prehospital environment by a road based trauma response team. Emerg med J. 2014;31 (7):583-8.
- Le Clerc S, McLennan J, Kyle A, Mann-Salinas E, Russell R. Predicting when to administer blood products during tactical aeromedical evacuation: evaluation of a U.S. model. J Spec Oper Med. 2014;14(4):48-52.
- Wheeler, AR, Cuenca C, Fisher AD et al. Development of prehospital assessment findings associated with massive transfusion. Transfusion. 2020;60:S70-S76.
- Bassett AK, Auten JD, Zieber TJ, Lunceford NL. Early, prehospital activation of the walking blood bank based on mechanism of injury improves time to fresh whole blood transfusion. J Spec Oper Med. 2016;16(2):5-8.
- Nunez TC, Voskresensky IV, Dossett LA, Shinall R, Dutton WD, Cotton BA. Early prediction of massive transfusion in trauma: simple as ABC (assessment of blood consumption)? J Trauma. 2009;66(2):346-52.
- Via DK. Urgent resuscitation using blood products during tactical evacuation from point of injury. CENTCOM Clinical Operating Protocols 2016;CCOP-01.
- JTS, Damage Control Resuscitation CPG, 12 Jul 2019.
- JTS, Frozen and Deglycerolized Red Blood Cells CPG, 11 Jul 2016
- JTS, Whole Blood Transfusions CPG, 15 May 2018.
- Hendrickson JE, Hillyer CD. Noninfectious serious hazards of transfusion. Anesth analg. 2009;108(3):759-69.
- Hendrickson JE, Roubinian NH, Chowdhury D, et al. Incidence of transfusion reactions: a multicenter study utilizing systematic active surveillance and expert adjudication. Transfusion. 2016;56(10):2587-96.
- Dutton RP, Shih D, Edelman BB, Hess J, Scalea TM. Safety of uncrossmatched type-O red cells for resuscitation from hemorrhagic shock. J Trauma. 2005;59(6):1445-9.
- Ho KM, Leonard AD. Concentration-dependent effect of hypocalcaemia on mortality of patients with critical bleeding requiring massive transfusion: a cohort study. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2011;39(1):46-54.
- Magnotti LJ, Bradburn EH, Webb DL, et al. Admission ionized calcium levels predict the need for multiple transfusions: a prospective study of 591 critically ill trauma patients. J Trauma. 2011;70(2):391-5; discussion 5-7.
- Vivien B, Langeron O, Morell E, et al. Early hypocalcemia in severe trauma. Crit Care Med. 2005;33(9):1946-52.
- Moore HB, Tessmer MT, Moore EE et al. Forgot calcium? Admission ionized-calcium in two civilian randomized controlled trials of prehospital plasma for traumatic hemorrhagic shock. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020;88:588-596)
- Giancarelli A, Birrer KL, Alban RF, Hobbs BP, Liu-DeRyke X. Hypocalcemia in trauma patients receiving massive transfusion. J surg res. 2016;202(1):182-7.
- MacKay EJ, Stubna MD, Holena DN, et al. Abnormal calcium levels during trauma resuscitation are associated with increased mortality, increased blood product use, and greater hospital resource consumption: a pilot investigation. Anesth Analg. 2017;125(3):895-901.
- Cherry RA, Bradburn E, Carney DE, et al. Do early ionized calcium levels really matter in trauma patients? J Trauma. 2006;61(4):774-9. doi:10.1097/01.ta.0000239516.49799.63.
- Long AM, Lefebvre CM, Masneri DA, et al. The golden opportunity: multidisciplinary simulation training improves trauma team efficiency. Journal of Surgical Education. 2019 Jul 1;76(4):1116-21.
- Fisher AD, Carius BM, Corley JB, et al. Conducting fresh whole blood transfusion training. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2019 Jul 1;87(1S):S184-90.
- Miles EA, Maitha JC. Optimal methods of teaching and training DCR/RDCR. Damage Control Resuscitation 2020 (pp. 339-354). Springer, Cham.
APPENDIX A: PREHOSPITAL BLOOD TRANSFUSION PROCEDURES
BEFORE
Criteria for Blood Transfusion:
- HR >100 bpm; or
- SBP <100 mmHg or no radial pulse; or
- Altered mental status with signs/symptoms hemorrhagic shock; or
- Penetrating trauma to chest/abdomen, junctional injuries; or
- Pelvic fracture; or
- Any above knee amputation or multiple amputations (regardless of vital signs)
DURING
- Obtain IV/IO access
- Verify blood product identification number
- Connect IV tubing with filter to blood
- Transfuse as rapidly as tolerated
- Monitor for signs of transfusion reaction: Hypotension, flushed face, wheezing, fever, rigors, flank pain
- Anaphylaxis = Epinephrine 0.3 mL of 1:1000 IM; Diphenhydramine 25 mg IV/IM; Maintain airway; Administer IV fluids prn; Consider Methylprednisolone
- Acute hemolytic reaction = Diphenhydramine 25 mg IV/IM; Consider osmotic diuresis with 20 gm mannitol 20% or 250 mL 3% NaCl
AFTER
Resupply from pre-designated source: Consider 1 gm Calcium IV
Abbreviations: Heart rate (HR), Beats per minute (bpm), Systolic blood pressure (SBP), Intravenous (IV), Intraosseous (IO), Intramuscular (IM), As needed (prn), Gram (gm), Sodium chloride (NaCl)
APPENDIX B: RESUSCITATION USING BLOOD PRODUCTS DURING TACEVAC
Source: Vampire Program: CENTCOM Clinical Operations Protocol-01: Urgent Resuscitation using Blood Products during Tactical Evacuation from Point of Injury
PURPOSE
To provide essential instructions on urgent/life-saving resuscitation procedures using blood products during tactical evacuation (refers to both casualty evacuation and medical evacuation) from the point of injury (POI) for casualties suffering major blood loss/massive hemorrhage. Referred to as the Vampire Program. This guideline supports the Joint Trauma System (JTS) Damage Control Resuscitation Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG), Whole Blood Transfusion CPG, and the Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC) Guidelines.
Guidance applies to medical and non-medical personnel (e.g., flight medic, crew chief, registered nurse, enlisted medical personnel, physician, nurse practitioner, or, physician assistant), assigned/attached or allocated to perform tactical medical response (TCCC) and evacuation (CASEVAC and MEDEVAC) duties that involve direct or indirect patient care.
FIELD INDICATIONS FOR TRANSFUSION DURING TACTICAL EVACUATION
The following are indications for transfusion in the presence of severe traumatic injury:
- Systolic BP <100 or absence of radial pulse; or
- Heart rate >100; or
- Any above knee amputation or double/triple/quadruple amputation (regardless of vital sign indication).
WARNING: The amputation patterns above are the only traumatic injuries that constitute a stand-alone immediate field indicator for transfusion that requires no confirmation with vital sign parameters.
CAUTION: Control external bleeding before or simultaneously with initiation of blood product transfusion.
Traumatic Arrest: patient with exsanguination who had signs of life when received from ground forces and has since become pulseless should receive immediate transfusion (transfusion is more important than chest compressions in cases of exsanguination and should take priority).
Traumatic injuries where early blood transfusions are most likely to be needed:
- Penetrating thoracic/abdominal/junctional (junctional includes axilla/inguinal/cervical) injury.
- Pelvic fracture.
- Multiple injuries.
- Proximal amputations (above knee or elbow). Amputation is defined as any severe trauma to a limb that involves complete or partial loss of the limb (this includes limbs that are severely mangled but not completely severed).
Initiate transfusion with 1 unit of blood product. Give additional units if clinically indicated. Avoid resuscitation with crystalloid which may increase bleeding, particularly from non-compressible torso hemorrhage.
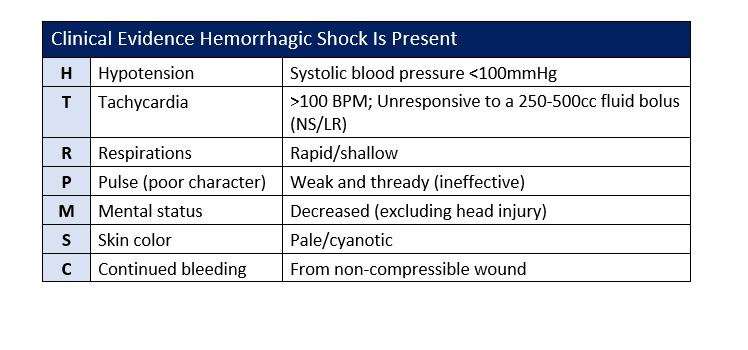
Refer to Appendix C for list of clinical indicators for hemorrhagic shock.
PROCEDURE
Blood Component Therapy Approved for Transfusion during Tactical Evacuation
Red blood cells (RBCs) increase the recipient’s oxygen-carrying capacity by increasing the mass of circulating red cells. Plasma and platelets work together to improve blood clot formation and clot stability. On average a unit of whole blood (WB) contains a volume of 500-600 mL and a unit of RBC’s contains a volume of 300-400 mL. In an exsanguinating patient, a unit of blood can be given quickly. Ensure good blood flow through IV or IO access before initiating transfusion. Refer to Appendix D for Transfusion Procedures and Appendix F for Pearls for Transfusion.
CAUTION: Rapid infusion against resistance can cause mechanical shearing of RBCs and should be avoided.
1. Blood products will be administered in the following priority depending on availability and according to TCCC Guidelines:
- Cold Stored Low titer Group O whole blood (LTOWB), or, if not available
- Fresh Low titer Group O whole blood (LTOWB), or, if not available
- Plasma, RBCs, and platelets in a 1:1:1 ratio, or, if not available
- Plasma and RBCs in 1:1 ratio, or, if not available
- Reconstituted dried plasma, liquid plasma, or, thawed plasma alone or RBCs alone, or, if not available
- Fresh group O (typed by Eldon card or equivalent) whole blood from unknown titer walking blood bank
NOTE: LTOWB has been screened for anti-A and anti-B antibodies; these units contained a low titer of anti-A and anti-B and are therefore considered a universal donor product that may be given to recipients of any blood type with a minimum risk for a minor ABO incompatibility (typically minor and most often subclinical clinical consequences). The whole blood supplied to MEDEVAC units will be exclusively drawn in the United States from the ASBP-approved sites and distributed in theater by the ASBP blood distribution system. The LTOWB units will be fully tested following FDA current guidelines.
2. POS (either low titer Group O WB or Type O RBCs) is the standard for transfusion during evacuation.
NOTE: Patients requiring blood can safely receive un-cross matched low titer Group O WB or Type O RBCs until type-specific products are available.
3. If available, use O NEG on females of childbearing potential age <50 years old. Inform receiving facility regarding female given O POS blood for documentation in the medical record. If a minimal amount (just a few milliliters) is given, consider Rhogam therapy. The immunologic consequences of administration of an entire unit of O POS whole blood or RBC to an O NEG female of child-bearing potential cannot safely be reversed with Rhogam. Treatment of exsanguination takes precedence over potential future pregnancy outcomes.
CAUTION: WB collected in theater will NOT be supplied for use onboard MEDEVAC aircraft.
Plasma is recognized as an important component in preventing and treating coagulopathy in trauma. On average a unit contains a volume of 200-250 mL and is transfused rapidly.
- Type A or AB thawed plasma is the current standard for transfusion during evacuation.
- Thawed plasma only has a shelf life of 5 days and may not be available for the pre-hospital mission. Liquid plasma (never frozen) has a shelf life of 26 days. Check with issuing facility or blood supply unit for availability.
The recommended mission loads for tactical evacuation are based on operations tempo and determined by the theater or Joint Task Force surgeon. Specific missions may require additional blood products; units will refer to the Joint Blood Program Office.
- Golden Hour Container (GHC) maximum capacity is 4 units RBC/FFP or 2 units of whole blood.
- If whole blood or plasma is unavailable, evacuation personnel will fly with RBCs exclusively.
- Product must finish infusion within 4 hours of spiking the bag. If not complete, then it needs to be stopped and the remainder of the product discarded. If the initiation of transfusion (spiking of the bag) is delayed, then the blood may be returned to storage if it hasn’t exceeded appropriate transport temperature, which is a max of 10C. The only way this can be determined is with use of a Safe-T-Vue sticker on the actual blood bag.
- Unused blood products (i.e. WB and freeze dried plasma [FDP]) furnished by forward U.S. or Coalition Forces will not be used by evacuation personnel. Recommend products be left with forward forces. Blood products (WB and FDP) spiked by forward forces and transfusing at time of pick up will be continued during evacuation.
Pediatric patients:
- Emergency transfusion of pediatric patients relies on clinical assessment rather than specific vital signs, since normal heart rate and blood pressure are age-dependent.
- Clinical signs of shock are the same as in adults (cool, pale, weak or absent radial pulse, delayed capillary refill, decreased mental status).
- Pediatric fluid resuscitation related to trauma begins with 10 mL/kg of first blood product, then repeat as needed based on response.
Receiving Blood Components from an Issuing Facility (U.S. and Coalition)
U.S. issuing facility personnel from the Blood Support Detachment (BSD), MTF (Role 2/3) or lab will:
- If requested and available, thaw frozen plasma IAW local procedures and label products (A or AB) with 5 day expiration date.
- Ensure GHC is properly charged and removed from freezer 25-30 minutes prior to loading blood products.
- Ensure all blood products issued have a Safe-T-VUE (NSN 6515-08-T00-3056) attached and activated for temperature monitoring (Appendix E). Ensure thawed plasma is at refrigerated temperature (1-6°C) before placing Safe-T-VUE on unit.
- Evacuation personnel will follow Safe-T-VUE procedures (Appendix E) when required.
- Document in TMDS the issuance of blood products to an evacuation team (e.g., DUSTOFF; Pararescue; Tactical Critical Care Evacuation Team).
- Complete appropriate sections of the SF 518 Blood or Blood Component Transfusion Record for issuing blood products; place inside GHC pocket or attach form to each unit of blood product issued.
- Verify the blood information on the SF 518 against the blood product label with receiving evacuation unit personnel.
Non-U.S. Issuing Facility: When U.S. blood products are to be issued from a Coalition facility, contact the Joint Blood Program Office to coordinate issuing requirements and documentation of units received.
Receiving unit (Evacuation Unit) personnel will:
- Prior to sealing GHC, ensure each blood product loaded into the GHC has an activated Safe-T-VUE attached (Appendix E) and an SF 518 Form.
- Accept blood products into receiving unit’s TMDS inventory. If receiving unit is unable to access TMDS, the issuing facility will access account and receive the products under the receiving unit’s TMDS inventory.
Storage, Transportation and Monitoring of Blood Products
- All blood and blood components must be maintained in a controlled environment and stored under appropriate conditions.
- Blood products carried outside a BSD/MTF/Lab will only be transported in an approved storage container (e.g., Golden Hour Container NSN 6530-01-505-5301; OCP/5306; Desert) for a maximum of 48 hours.
- Units will monitor containers and document status (e.g., dry/no leaking noted) at a minimum of every 24 hours.
- Once loaded and sealed, container will remain closed and intact at all times until blood product is required for patient care.
- Notify the issuing facility (BSD/MTF/Lab) as soon as possible when blood products have been used.
- GHC is only approved for 48 hours use; prior to expiration end users will contact issuing facility (BSD/MTF/LAB) to coordinate the return and exchange of a container and blood products per mission requirements.
WARNINGS: - At no time will container or its contents (blood products) be placed in a refrigerator or other cooling device outside a blood bank. - Blood products will not be used if container is leaking; or the temperature indicator (Safe-T-VUE) on the blood product is out of standard (refer to Appendix E). - Notify the issuing facility and return container and products for replacement.
Individual and Unit Training Requirements
- At a minimum, medical personnel who participate in the administration of blood products during evacuation will be trained in the following topics:
- Indications for transfusion (Appendix C)
- Transfusion procedures (Appendix D);
- Documentation (Appendix G)
- PEARLS for transfusion (Appendix F)
- Submission of a patient safety report when required
- At a minimum, non-medical personnel who assist will be trained in the following:
- Transfusion procedures
- Equipment/supplies
- Documentation requirements for the SF 518
- Units who implement this CPG will train appropriate personnel on the following:
- Emergency procedures for in-flight complications.
- Storage container/blood product exchange requirements.
Essential Items Required for Implementing a Vampire Program
- Approved blood component transport container.
- Recommend between 4 and 6 each GHCs for a Vampire Program (NSN 6530-01-505-5301 (OCP)/5306(Desert)).
- Hemacool (NSN 4110-01-506-0895) or other freezer with temp check to ensure a temperature ≤ to (-) 18°C to support reconditioning of GHC.
- Safe-T-VUE (NSN 6515-08-T00-3056) for temperature monitoring. (Refer to Appendix E.)
- Establish Theater Medical Data Store (TMDS) accounts for an issuing facility (BSD/MTF (Role2/3) and LAB); and receiving unit (evacuation unit)
Warming Devices for Blood Transfusion
Use of infusion warming devices is highly recommended. These will be FDA approved for the actual use in transfusion of blood products (examples of devices include: Belmont® Buddy-lite™, EnFlow® or Thermal Angel).
WARNING: Warming devices will have safety mechanisms built in that prevents the output temperature from exceeding 42°C. Unit personnel will be familiar with safety mechanisms for the device used.
Tranexamic Acid (TXA)
Patients receiving blood transfusion within three hours of injury should also receive TXA. Refer to the TCCC guidelines for administration of TXA.
Record Keeping and Documentation Requirements
- Transfusions will be documented into TMDS by evacuation personnel, or, by issuing facility.
- Personnel will refer to the Theater Blood Application Training Guide, 02 Jun 2014 for directions on Inventory Management-and for Transfused Products.
- Complete SF 518 documentation and turn over at the destination MTF for placement in the patient’s medical record.
References
- Armed Services Blood Program (ASBP), Joint Blood Program Handbook, HQ Departments of the Army, Navy and Air Force (Army Technical Manual 8-227-12, NAVMED P-6530, AFH 44-152-IP), 01 Dec 2011.
- Central Command Regulation (CCR) 40-1, Quality Management (QM) Programs in Healthcare Operations, 19 Feb 2016.
- CCR 40-4, Clinical Operations (CLINOPS) Program, Jan 2016.
APPENDIX C: CLINICAL INDICATIONS OF HEMORRHAGIC SHOCK
APPENDIX D: TRANSFUSION PROCEDURES

APPENDIX E: SAFE-T-VUE-TEMPERATURE INDICATOR
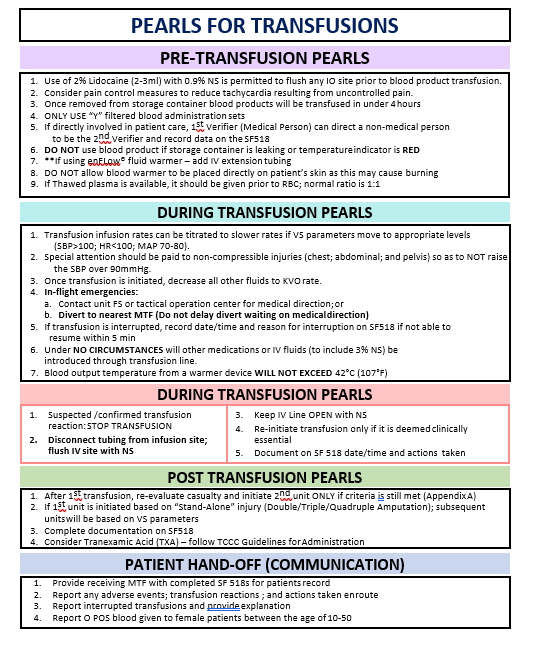
APPENDIX F: PEARLS FOR TRANSFUSIONS
APPENDIX G: REQUIRED DOCUMENTATION FOR TRANSFUSION
- SF 518 Blood or Blood Component Transfusion Record ASBP
- 151 Whole Blood Transfusion Checklist
- 147 Eldon Card ABO/Rh Typing Record
- 145 Infectious Disease Testing for Blood Donation
- 148 Pre-screen Whole Blood Sample Shipping Manifest
- 150A Emergency Release Letter of Understanding (tested)
- 150B Emergency Release Letter of Understanding (untested)
- 572 Emergency Whole Blood Donation Record
- AABB Medications Deferral List
- DHQ Medication Deferral List
APPENDIX H: ADDITIONAL INFORMATION REGARDING OFF-LABEL USES IN CPGS
Purpose
The purpose of this Appendix is to ensure an understanding of DoD policy and practice regarding inclusion in CPGs of “off-label” uses of U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved products. This applies to off-label uses with patients who are armed forces members.
Background
Unapproved (i.e. “off-label”) uses of FDA-approved products are extremely common in American medicine and are usually not subject to any special regulations. However, under Federal law, in some circumstances, unapproved uses of approved drugs are subject to FDA regulations governing “investigational new drugs.” These circumstances include such uses as part of clinical trials, and in the military context, command required, unapproved uses. Some command requested unapproved uses may also be subject to special regulations.
Additional Information Regarding Off-Label Uses in CPGs
The inclusion in CPGs of off-label uses is not a clinical trial, nor is it a command request or requirement. Further, it does not imply that the Military Health System requires that use by DoD health care practitioners or considers it to be the “standard of care.” Rather, the inclusion in CPGs of off-label uses is to inform the clinical judgment of the responsible health care practitioner by providing information regarding potential risks and benefits of treatment alternatives. The decision is for the clinical judgment of the responsible health care practitioner within the practitioner-patient relationship.
Additional Procedures
Balanced Discussion
Consistent with this purpose, CPG discussions of off-label uses specifically state that they are uses not approved by the FDA. Further, such discussions are balanced in the presentation of appropriate clinical study data, including any such data that suggest caution in the use of the product and specifically including any FDA-issued warnings.
Quality Assurance Monitoring
With respect to such off-label uses, DoD procedure is to maintain a regular system of quality assurance monitoring of outcomes and known potential adverse events. For this reason, the importance of accurate clinical records is underscored.
Information to Patients
Good clinical practice includes the provision of appropriate information to patients. Each CPG discussing an unusual off-label use will address the issue of information to patients. When practicable, consideration will be given to including in an appendix an appropriate information sheet for distribution to patients, whether before or after use of the product. Information to patients should address in plain language: a) that the use is not approved by the FDA; b) the reasons why a DoD health care practitioner would decide to use the product for this purpose; and c) the potential risks associated with such use.
